In the fast-paced realm of engineering and simulation, clear data visualization is crucial. Femap 2306 color groups play a vital role in making sense of intricate simulation results, allowing engineers and designers to glean essential insights from their data with precision. This article explores the significance of Femap color groups, offers guidance on their effective use, and highlights their practical applications, all aimed at enhancing your modeling and analysis efforts.
The Value of Color Groups in Femap 2306
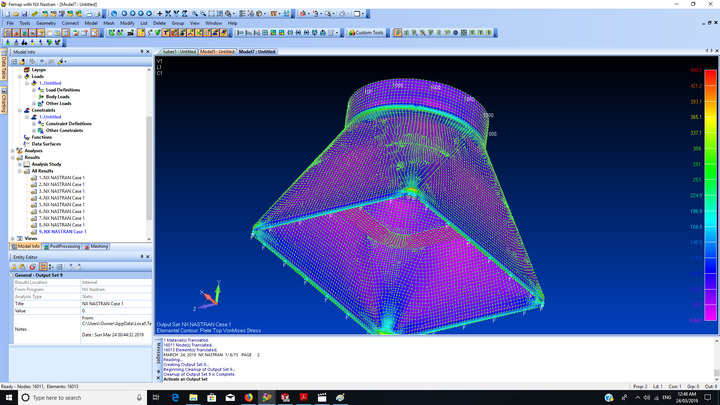
Femap 2306 color groups are unique sets of colors designed to improve the visualization of simulation data. These color codes serve as a visual shorthand, enabling users to swiftly recognize different parameters in their analyses. For example, bright reds may signal high-stress areas, while soothing blues can indicate safe zones. This instant recognition simplifies the process of interpreting complex data, allowing users to quickly identify critical issues.
By utilizing these color groups, engineers can efficiently categorize simulation results. This approach not only accelerates the identification of potential problems but also aids in comparing various scenarios. The ability to see the effects of design changes or material selections through color-coded outputs makes decision-making smoother and leads to better project outcomes.
Additionally, employing color groups elevates the presentation of technical information. Instead of sifting through spreadsheets filled with numbers and graphs, stakeholders can access clear, vibrant visuals that underscore key findings. This visual clarity promotes more engaging discussions among team members and clients, enhancing collaboration and ensuring a shared understanding of the analysis.
Comprehending Color Groups in Femap 2306
At its essence, Femap 2306 color groups offer a systematic way to visualize simulation results. Each color is linked to specific data points or performance metrics, establishing an intuitive framework for analysis. This color coding not only facilitates quick evaluations but also improves the communication of findings.
When engineers look at a model adorned with distinct color groups, they can swiftly understand the condition of various parameters. For example, deep red might indicate areas under significant stress, while light green could represent zones performing optimally. This type of immediate visual feedback is crucial in a field where both time and accuracy are paramount.
Moreover, Femap color groups allow users to tailor their visualizations to meet project-specific requirements. Whether it involves selecting a specific color palette or creating gradients to represent varying performance levels, this customization ensures that the visuals are both meaningful and relevant to the analysis being conducted.
Color Groups’ Importance in Analysis
Color groups are essential for simplifying the complex data landscape of Femap analysis. They enable users to convert intricate numerical data into visually clear formats, making it easier to identify potential issues and trends. For instance, a sudden cluster of red areas in a simulation can quickly indicate a design flaw that needs addressing.
Furthermore, color groups enhance comparative analysis across different scenarios. By using distinct colors for varying datasets, users can rapidly evaluate the effects of design modifications or environmental changes on performance. This visual clarity not only helps in pinpointing optimal solutions but also fosters informed decision-making.
Additionally, effective use of color significantly boosts collaborative efforts. When sharing findings, vibrant visuals allow stakeholders to grasp key points swiftly. This results in more focused discussions and quicker conclusions, as everyone can see the critical data visually rather than sifting through numbers alone.
Changing the Color Groups in Femap 2306
A key feature of Femap 2306 is its customization of color groups, allowing users to adapt them to the specific requirements of their projects. This flexibility enables the selection of colors that align with your objectives—such as using green for safe zones and red for high-risk areas—making it easier to highlight critical data.
To adjust the colors, simply head to the settings menu within Femap. This interface offers a range of color choices, allowing you to create gradients that effectively represent different values. For instance, you might use lighter shades for lower values and deeper hues for higher ones, providing a more detailed perspective on your data that enhances your analysis.
It’s also important to keep your audience in mind when selecting color schemes. Choosing colors that are easy to distinguish and not overly bright can improve readability. Additionally, being aware of color blindness ensures that your visuals are accessible to all viewers, maximizing the effectiveness of your presentations.
The Best Ways to Use Color Groups in Femap 2306
To maximize the effectiveness of Femap 2306 color groups, it’s important to follow these best practices:
- Select Meaningful Colors: Choose colors that intuitively communicate their significance. For instance, use warm tones like red and orange to signify danger, while cooler hues like blue and green can indicate safety. This approach helps viewers quickly grasp the implications of the data.
- Ensure Consistency: Consistency is crucial in color coding. If a certain color represents high stress in one part of your model, it should have the same meaning throughout the entire analysis. This uniformity minimizes confusion and enhances overall understanding.
- Incorporate Labels and Legends: While colors can provide quick insights, labels offer more detailed information. Including a legend that explains the color scheme helps ensure that viewers accurately interpret your visuals, further improving comprehension.
- Test Your Color Selections: Always check how your chosen colors appear across different screens and in printed formats. Colors can look different depending on the medium, so it’s essential to ensure visibility and clarity across all platforms for effective communication.
- Limit Color Diversity: Avoid overwhelming your audience with too many colors. Stick to a limited palette that clearly conveys your message. Using a few well-defined colors to represent different categories keeps your analysis straightforward and focused.
By following these best practices, you can significantly improve the clarity and impact of your Femap 2306 analysis.
Typical Mistakes Made When Using Femap Color Groups
While Femap color groups offer numerous advantages, users frequently encounter common mistakes. Here are some pitfalls to avoid:
- Choosing Similar Colors: One major error is selecting colors that are too similar. When shades are barely distinguishable, it can be challenging for viewers to differentiate between data points. Opting for distinct colors helps ensure clarity in your analysis.
- Overusing Color: Although color is a powerful visualization tool, using too many can create confusion. A streamlined palette that effectively communicates your message is usually more impactful. A few strong colors are often more effective than an overwhelming variety.
- Neglecting to Test Colors: Sometimes, users forget to check how their color choices appear on different platforms. Testing is essential, as colors can vary significantly depending on the viewing medium. Ensuring that your selections work well in all contexts helps prevent miscommunication.
- Ignoring Context: Not considering the context in which colors are applied can lead to misunderstandings. Always assess how the colors interact with one another within the broader model for a clearer overall picture.
By being mindful of these common mistakes, you can use Femap color groups more effectively and create visuals that are both clear and impactful.
Applications of Femap 2306 Color Groups in the Real World
Femap 2306 color groups are utilized in a range of industries, showcasing their adaptability. In engineering, for instance, these color codes help visualize stress distribution in structures, enabling engineers to pinpoint areas experiencing excessive pressure. This valuable insight allows for timely adjustments before construction begins, thereby enhancing both safety and efficiency.
In the realm of product design, color groups play a crucial role in differentiating materials and their properties. Designers can visually assess how various materials respond to stress, providing teams with critical information that supports informed design choices.
Environmental studies also reap the benefits of Femap color groups. Researchers use color coding to illustrate pollution levels across different areas, employing bright colors to signify high pollution and softer shades for cleaner regions. This visual representation empowers communities to recognize environmental issues and motivates action toward improvement.
Overall, from engineering and product design to environmental science, Femap 2306 color groups deliver essential insights that facilitate better decision-making and outcomes.
Comprehending Color Psychology in Femap
The psychology of color plays a crucial role in how effectively Femap 2306 color groups convey information. Different colors can trigger various emotional responses; for instance, red is often associated with urgency or danger, while blue tends to evoke feelings of calmness and stability. By grasping these psychological effects, you can choose colors that effectively communicate your intended message.
When selecting colors, consider the emotional impact you want to achieve with your audience. For instance, to draw attention to issues, bold colors like red or yellow may be ideal, whereas softer tones like green and blue can provide a sense of safety and reassurance. This deliberate choice enhances the overall effectiveness of your communication.
It’s also important to recognize that color perception can vary significantly across cultures. For example, while white is often seen as a symbol of purity in some cultures, it may represent mourning in others. Being mindful of your audience’s cultural background can help ensure that your color selections resonate well and avoid potential misunderstandings.
Understanding the Color Group Outputs of Femap 2306
Interpreting outputs from Femap 2306 color groups is a crucial skill for users. When you examine a colored model, start by understanding what each color signifies. For instance, if red denotes high stress and blue represents low stress, you can swiftly identify areas that require your attention.
It’s also important to consider the intensity of the colors. Darker shades typically indicate more severe issues, while lighter shades suggest less critical areas. Being able to recognize these differences helps you prioritize your responses based on the level of concern.
Additionally, look at the context of your data. Analyze how the colors interact within the overall model, as this can reveal patterns or trends that may not be immediately apparent. Having a comprehensive view is essential for making informed decisions based on your analysis.
Making Visuals Better Using Femap Color Groups
To enhance your visualization with Femap 2306 color groups, consider these helpful tips:
- Leverage Color Contrasts: Using contrasting colors effectively can significantly improve visual clarity. Choose colors that stand out from one another, making it easier for viewers to distinguish between different data points. High contrast not only captures attention but also aids in quick comprehension.
- Add Legends and Labels: Including a legend that explains the meaning of each color provides essential context, ensuring viewers accurately interpret your visuals. Clear labels can also emphasize key findings, guiding your audience to focus on the most critical information.
- Incorporate Interactive Features: If feasible, consider adding animations or interactive elements to your visualizations. These features allow users to engage with the data in real time, creating a more dynamic and informative experience.
By applying these strategies, you can enhance the effectiveness of your Femap 2306 analysis and make it more accessible for your audience.
Femap 2306 Color Group Comparison with Other Programs
When comparing Femap 2306 color groups to those found in other simulation software, several important distinctions become apparent. While many tools offer some form of color coding, Femap is particularly notable for its flexibility and ease of customization. Users can easily adjust colors to fit their specific requirements, a feature that isn’t always as user-friendly in other programs.
Moreover, Femap is recognized for its clear and intuitive visual representations. The color groups are thoughtfully designed to enable quick identification of issues, whereas other software might use colors that are too similar, complicating interpretation. This clarity is crucial for effective analysis and sound decision-making.
Additionally, Femap integrates smoothly with other engineering tools, allowing for straightforward sharing of color-coded outputs among team members using different software. This level of compatibility is vital for collaboration, ensuring that everyone can easily understand the results without any confusion.
Upcoming Developments in Femap-Based Simulation Visualization
The future of simulation visualization with Femap 2306 color groups looks promising, with several exciting trends emerging. One major development is the integration of artificial intelligence (AI) to enhance data visualization. AI can process extensive datasets and recommend optimal color schemes, which can significantly improve both clarity and the overall quality of presentations.
Another key trend is the increasing focus on user experience design. As software becomes more user-friendly, there’s a growing expectation for better navigation and clearer visuals. Femap is likely to continue advancing in this area, making it simpler for users to interpret their results through well-designed color groups.
Additionally, the rise of virtual reality (VR) and augmented reality (AR) technologies in engineering and simulation opens up new avenues for interaction. These immersive technologies allow users to engage with their models in innovative ways, incorporating color groups to enhance data exploration and understanding.
Conclusion
In conclusion, Femap 2306 color groups are essential tools for anyone dealing with simulation data. They transform complex information into easily digestible visuals, allowing for quick identification of key insights and supporting informed decision-making. By utilizing these color groups, engineers and designers can craft engaging visuals that enhance presentations and stimulate productive discussions.
Mastering Femap color groups can greatly influence the effectiveness of your analyses, leading to improved project outcomes. By choosing the right colors, ensuring consistency, and being mindful of your audience, you can elevate your visualizations and enrich your overall simulation experience. As simulation technology continues to advance, keeping up with these changes will help you stay ahead in the realm of effective data analysis.